Products
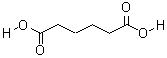
Adipic acid.(CAS:124-04-9)
Uses
Adipic acid can undergo salt-forming reactions, esterification reactions, amidation reactions, etc., and can be polycondensed with diamines or glycols to form high-molecular polymers. Adipic acid is a dicarboxylic acid of great industrial significance. It plays an important role in chemical production, organic synthesis industry, medicine, and lubricant manufacturing. Adipic acid is also a raw material for medicine, yeast purification, pesticides, adhesives, synthetic leather, synthetic dyes and perfumes.
Adipic acid is mainly used as a raw material for nylon 66 and engineering plastics. It is also used for the production of various ester products. It is also used as a raw material for polyurethane elastomers and as an acidifier for various foods and beverages. Over citric acid and tartaric acid.
Adipic acid is also a raw material for medicine, yeast purification, pesticides, adhesives, synthetic leather, synthetic dyes and perfumes.
Adipic acid has a soft and long-lasting sour taste, and the pH value changes less in a larger concentration range. It is a better pH value regulator. GB2760-2007 stipulates that the maximum usage amount of this product for solid beverages is 0.01g/kg; it can also be used for jelly and jelly powder, and the maximum usage amount for jelly is 0.01g/kg; when it is used for jelly powder, it can be pressed Adjust the multiple to increase the usage.
Adipic acid or hexanedioic acid is the organic compound with the formula
(CH2)4(COOH)2. From an industrial perspective, it is the most important dicarboxylic acid: about 2.5 billion kilograms of this white crystalline powder are produced annually, mainly as a precursor for the production of nylon. Adipic acid otherwise rarely occurs in nature, but it is known as manufactured E number food additive E355.
About 60% of the 2.5 billion kg of adipic acid produced annually is used as monomer for the production of nylon by a polycondensation reaction with hexamethylene diamine forming nylon 66. Other major applications also involve polymers; it is a monomer for production of polyurethane and its esters are plasticizers, especially in PVC.
Application
Adipic acid is mainly used as a raw material for nylon 66 and engineering plastics. It is also used for the production of various ester products. It is also used as a raw material for polyurethane elastomers and as an acidifier for various foods and beverages. Over citric acid and tartaric acid.
Adipic acid is also a raw material for medicine, yeast purification, pesticides, adhesives, synthetic leather, synthetic dyes and perfumes.
Adipic acid has a soft and long-lasting sour taste, and the pH value changes less in a larger concentration range. It is a better pH value regulator. GB2760-2007 stipulates that the maximum usage amount of this product for solid beverages is 0.01g/kg; it can also be used for jelly and jelly powder, and the maximum usage amount for jelly is 0.01g/kg; when it is used for jelly powder, it can be pressed Adjust the multiple to increase the usage.
In medicine:
Adipic acid has been incorporated into controlled-release formulation matrix tablets to obtain pH-independent release for both weakly basic and weakly acidic drugs. It has also been incorporated into the polymeric coating of hydrophilic monolithic systems to modulate the intragel pH, resulting in zero-order release of a hydrophilic drug. The disintegration at intestinal pH of the enteric polymer shellac has been reported to improve when adipic acid was used as a pore-forming agent without affecting release in the acidic media. Other controlled-release formulations have included adipic acid with the intention of obtaining a late-burst release profile.
In foods:
Small but significant amounts of adipic acid are used as a food ingredient as a flavorant and gelling aid. It is used in some calcium carbonate antacids to make them tart. As an acidulant in baking powders, it avoids the undesirable hygroscopic properties of tartaric acid. Adipic acid, rare in nature, does occur naturally in beets, but this is not an economical source for commerce compared to industrial synthesis.
Safety care:
Adipic acid, like most carboxylic acids, is a mild skin irritant. It is mildly toxic, with a median lethal dose of 3600 mg/kg for oral ingestion by rats.
Environmental issues:
The production of adipic acid is linked to emissions of N2O, a potent
greenhouse gas and cause of stratospheric ozone depletion. At adipic acid producers DuPont and Rhodia (now Invista and Solvay, respectively), processes have been implemented to catalytically convert the nitrous oxide to innocuous products:
2 N2O → 2 N2 + O2